As the program year winds down, implementation staff find themselves in another busy season, inclusive of several data related initiatives. During the period between April and July, implementation leadership should continue their focus on fostering high levels of pair engagement and leveraging data to make informed decisions around classroom facilitation and pair support. Additionally, implementation staff are responsible for supplying quality assessments during the spring. This article outlines discrete leaderhip tasks associated with execution of spring data-related initiatives.
Spring at a glance
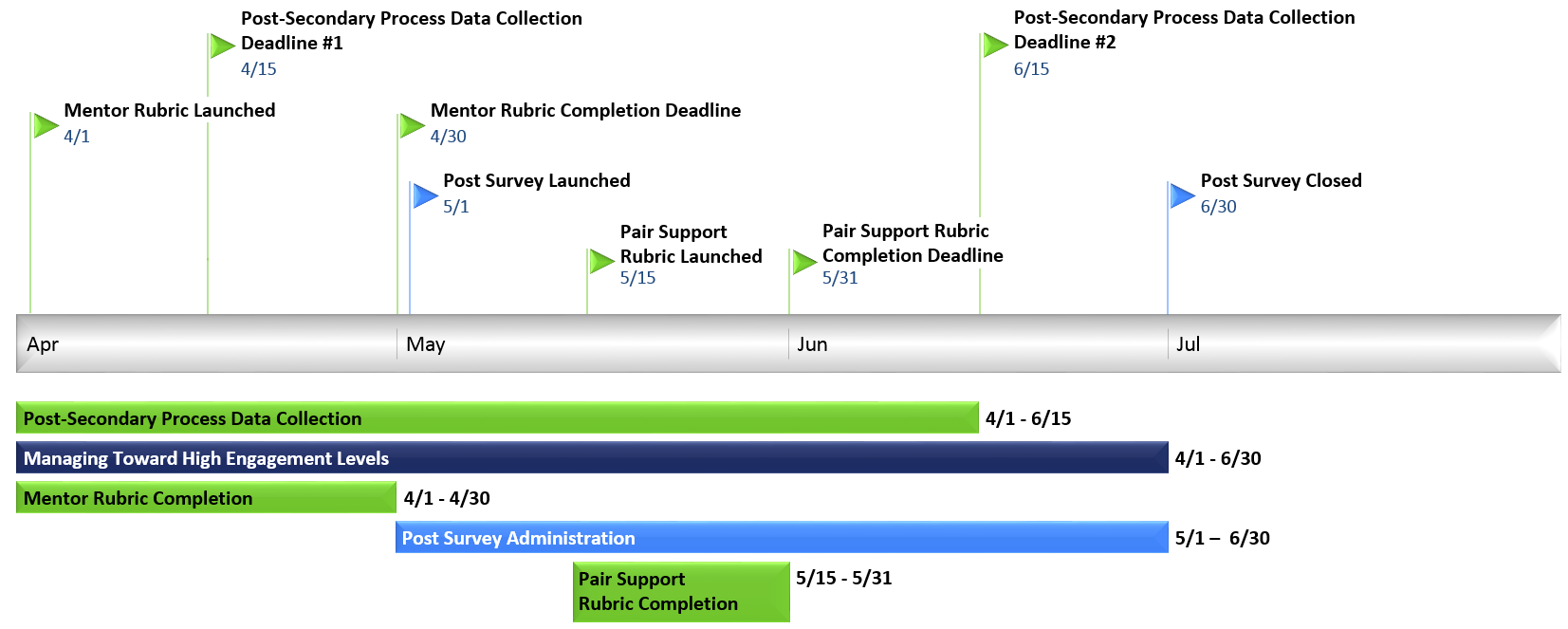
Spring leadership checklist
At any given point in the spring, the bars in the graphic above show where data driven management focus should be placed. The action items below should be regularly incorporated into management efforts as the program year nears its end.

Consistency is one of the most critical aspects of mentoring relationships and monitoring pair engagement is the most effective way to ensure mentees and mentors are regularly communicating. By the spring of each program year, robust pair engagement trends will have developed and it is important that implementation leaders regularly share best practices, challenges and strategies to increase and/or maintain pair engagement rooted in these trends. It is equally important that implementation leaders are held accountable for for meeting benchmarks. Managing engagement is particularly critical as the program year comes to a close and pairs approach the summer lull in communication.
The Mentor Quality Rubric requires implementation staff to assess the overall quality of their mentor population. The Pair Support Quality Rubric requires implementation leaders to assess the overall quality of implementation staff. The execution of these tasks is primarily motivated by the collection of important data that allows the organization to explore relationships between mentor/staff quality and mentee outcomes. However, it also offers a formal opportunity to reflect on the quality of mentors/staff to drive management efforts. From a data integrity perspective, it is essential that these rubrics be completed in the allotted time frame and management toward completion should be a unified leadership effort.

Still have questions?
Reach out to [email protected]. The team is more than happy to address any questions, comments or concerns you may have!